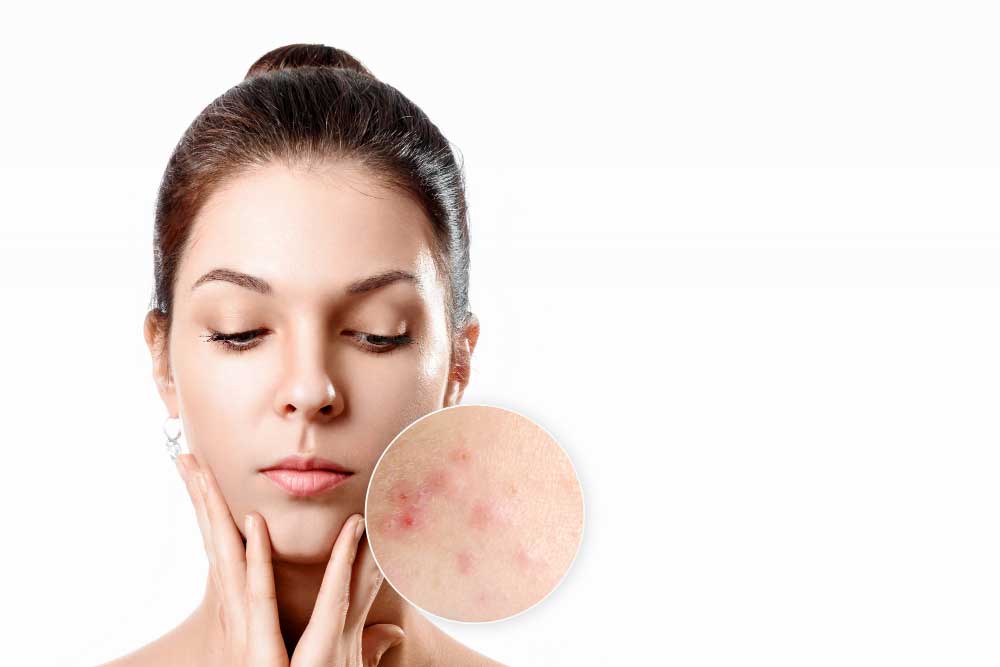
When hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, they cause acne. The sebaceous glands in our skin produce sebum, an oil that helps to keep our skin moisturized and healthy. However, when too much sebum is produced, it can mix with dead skin cells and bacteria, leading to inflammation and the formation of acne.
Hormones are a major contributor to acne, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. Hormonal changes can increase the production of sebum and cause the skin to become more sensitive to acne-causing bacteria.
Genetics also play a role in acne, as studies have shown that people with a family history of acne are more likely to develop it themselves. Lifestyle factors such as diet, stress, and skincare routine can also impact the severity of acne.
Common Myths about Acne
There are many misconceptions about acne that can make it difficult to treat and manage. Here are some of the common myths:
- Myth #1: Acne is caused by poor hygiene and climate. While it’s important to keep your skin clean, acne is not caused by dirt or sweat. In fact, over-cleansing or using harsh products can actually make acne worse.
- Myth #2: Eating greasy or fried foods causes acne. While certain foods may trigger acne in some people, there is no direct link between diet and acne. However, a healthy and balanced diet can help to improve overall skin health.
- Myth #3: Sun exposure can cure acne. While the sun can temporarily improve acne by drying out the skin, it can also cause long-term damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Types of Acne
Acne can present itself in different forms, each with its own characteristics and treatment options.
- Blackheads: these are small, dark bumps that form when a hair follicle becomes clogged with oil and dead skin cells. They are not raised and do not contain pus.
- Whiteheads: these are similar to blackheads.They appear as small, white bumps and can be difficult to extract.
- Pimples: these are inflamed lesions that can be red, swollen, and painful. They can contain pus and may leave a scar if not treated properly.
- Cysts: these are large, painful lumps that form deep under the skin. They can be filled with pus or a clear liquid and may require professional treatment.
- Nodules: these are similar to cysts but are harder and deeper. They can be painful and cause scarring.
The Impact of Diet on Acne
While there is no direct link between diet and acne, certain foods can trigger or worsen acne in some people. These include:
- Dairy products: milk, cheese, and yogurt can contain hormones that can increase sebum production and inflammation.
- High-glycemic foods: such as white bread, sugar, and potatoes can cause a spike in insulin levels, which can lead to increased sebum production.
- Processed foods: such as chips, candy, and fast food can contain additives and preservatives that can irritate the skin.
On the other hand, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein can help to improve overall skin health and reduce inflammation.
Skincare Routine for Acne-Prone Skin
A proper skincare routine can help to prevent and manage acne. Here are some tips:
- Cleanse gently: use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser twice a day to remove dirt and oil from the skin.
- Exfoliate carefully: use a gentle exfoliant once or twice a week to remove dead skin cells and unclog pores. Avoid over-exfoliating, as this can irritate the skin.
- Moisturize regularly: use a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated without clogging pores.
- Use sunscreen: choose a non-comedogenic sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to protect the skin from sun damage.
The Latest Treatments for Acne
There are many treatment options for acne, ranging from over-the-counter products to prescription medications and natural remedies.
- Over-the-counter products: such as benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, and retinoids can help to unclog pores and reduce inflammation. They are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate acne.
- Prescription medications: such as antibiotics, hormonal therapy, and isotretinoin can be prescribed by a dermatologist for more severe acne. These medications may have side effects and require close monitoring.
- Natural remedies: such as tea tree oil, aloe vera, and honey can also be used to treat acne. These remedies are generally safe and can help to soothe and heal the skin.
You can buy A-Ret 0.1% Gel online. A-Ret 0.1% Gel is used to treat acne. It contains Tretinoin (0.1% w/w). This gel is supplied online by Melon GlobalCare. Melon GlobalCare is a well-established healthcare brand and one of the world’s upcoming distributors in the pharmaceutical industry. They offer the finest Medical Facilities and provide the highest quality medications at reasonable prices.
You can buy it using the link below: A-Ret 0.1% Gel exporter in india
https://www.melonglobalcare.com/product/tretinoin-a-ret-gel-bulk-cargo-exporte